| |
 |
On subanalytic solutions of linear difference equations with polynomial coefficients
|
| |
|
S.A.Abramov( Computing Centre of RAS and MSU ) |
| |
|
|
|
|
We consider the space of subanalytic sequential solutions of linear difference equations with polynomial coefficients. The results presented in the talk were obtained by the author jointly with M. Barkatou, M. van Hoeij, M.
Petkovsek
.
|
| |
|
|
| |
 |
Algorithm of Computation of Power Transformations for
Analysing ODE Systems Near Infinitely Far Stationary Points
|
| |
|
A.B.Aranson ( Scientific Research Institute of Long-Range Radio Communication, Moscow) |
| |
|
|
|
|
An autonomous ODE system with polynomial right hand sides is considered. The method of normal form is used for analysing the system near its stationary point neighbourhood. For analysing near infinitely far stationary point it is necessary to translate the point to finite range. It can be done by means of power transformations. We suggest an algorithm of calculation of power transformations using the Newton-Bruno polyhedrons. This algorithm is implemented as collection of procedures of the "Maxima" computer algebra system. Application of this algorithm for Analysing the Henon-Heiles system is considered. |
| |
|
|
| |
 |
Reduced Forms of Systems of Linear Functional Equations and Applications |
| |
|
M. A. BARKATOU
( Universite de Limoges, XLIM, France ) |
| |
|
|
|
|
Moser and super-irreducible forms play a central role in the local analysis (and hence in the global study) of liner systems of differential or difference equations. Algorithms for constructing such forms have been developed and implemented in the Maple package ISOLDE.
In this talk, we shall explain how these concepts can be extended to the general class of \emph{systems of pseudo-linear equations} which comprises common types of systems
such as linear differential, difference or $q-$difference systems. For this we first introduce a
unifying framework that permits us to treat, simultaneously, all
types of linear functional systems. This is done by using the
language of pseudo-linear derivations over a field of discrete
valuation. We derive a definition of regularity and develop a method for recognizing regular
systems inspired by Moser's work on differential equations. As an application we shall show that the approach developed in the past for computing polynomial solution (and more generally formal series solutions at infinity) for differential and difference systems is also applicable for $q-$difference systems.
This talk is based on a recent joint work with E. Pfluegel and G. Broughton.
|
| |
|
|
| |
 |
A new block algorithm for solving sparce linear systems over GF(2) |
| |
|
М.А. Cherepniov( Moscow State University, mech-math. faculty ) |
| |
|
|
| |
|
This algorithm construct with the use of block Pade approximations. Running
time for parallel vertion bound by max{N2d/n, O(N2)},
where N - system matrix size, n - block size, d - upper bound for the number
of units in the rows of matrix.
|
| |
|
|
| |
 |
On the economiztion problem for polynomials of many variables |
| |
|
V.F.Edneral (SINP MSU), N.N.Vasilev (PDMI RAN) |
| |
|
|
| |
|
Quite often in applied problems it is necessary to make massive calculations of polynomials or rational functions of many variables. Problems of multidimensional integration on phase space are that, for example, at calculation of contributions to cross sections of particles scattering from sets of Feynman diagrams. Often there is a question on approximation of corresponding polynomials, by polynomials with essentially smaller supports. Sometimes such problem names a problem of economization of polynomials. A special case is well-known Lanczos method for approximation of a polynomial from one variable by a polynomial of smaller degree. For polynomials from several variables not trivial moment is the choice of the support of an approximating polynomial. We offer the approach in which the support of an approximating polynomial gets out on border of the Newton-Bruno polyhedron or near to this border. The algorithm of the multidimensional approximation with the fixed support in the uniform metrics is based on reducing to a problem of linear programming. |
| |
|
|
| |
 |
Computer Algebra Aspects of Fukaya Categories |
| |
|
N. M. Glazunov
( National Aviation University, Kiev, Ukraine) |
| |
|
|
| |
|
Fukaya Category is a homological algebra framework for
Lagrangian submanifolds
and their morphisms. We investigate computer algebra aspects of the
categories.
|
| |
|
|
| |
 |
A symbolic-numerical algorithm for a reduction of the two-dimensional
boundary problem to the ordinary differential equations |
| |
|
S.I. Vinitsky, V.P. Gerdt, A.A. Gusev, V.A. Rostovtsev, O.
Chuluunbaatar(JINR) |
| |
|
|
| |
|
A symbolic-numerical algorithm a reduction of the
two-dimensional boundary problem
to the second-order ordinary radial differential equations
with homogeneous boundary conditions of third type in bound
points of finite interval using a basis of the oblate angular
spheroidal functions is presented.
The recurrence relations for calculation with a given accuracy of
asymptotic expansions of required solution by angular and radial
variables at small and large values of radial
variable including threshold
values of spectral parameter of continuous spectrum are constructed.
The efficiency of algorithm is demonstrated by a test calculations and
visualization of asymtotic expansions of the two-dimensional solutions.
|
| |
|
|
| |
 |
Symbolic-numerical algorithm for constructing matrices stabilizing functional in the problem of restoring the surface
|
| |
|
M.G.Kokotchikova,
L.A.Sevastianov , D.S.Kulyabov
(People's Friendship University of Russia
) |
| |
|
|
| |
|
While restoring a surface one deals with instability of the procedure which must be excluded. We use the Tikhonov regularization method based on stabilizing functional. The restored surface is constructed with the help of Fourier coefficients in Zernike basis. In the report we present the symbolic-numerical algorithm for constructing matrices stabilizing functional realized in Computer Algebra System AXIOM.
|
| |
|
|
| |
 |
Gauge Invariance in Discrete Dynamical Systems
|
| |
|
V.V.Kornyak
(Laboratory of Information Technologies
Joint Institute for Nuclear Research) |
| |
|
|
| |
|
The fundamental laws of physics are described from the modern point of view by gauge theories with continuous gauge groups. We consider specifics of introduction of gauge invariance into discrete dynamical systems with finite sets of states. Typical examples of such systems are cellular automata.
|
| |
|
|
| |
 |
Mathematica Implementation of M. Bronstein's Poor Man's Integrator
Parallel Integration Method – Risch Norman Algorithm
|
| |
|
R. Kragler (Weingarten Univ. of Applied Sciences, Germany) |
| |
|
|
| |
|
In May 2005 Manuel Bronstein presented on the same CAS seminar in Dubna his implementation of the so-called "Poor Man's Integrator".
The method of "Parallel Integration" which goes back to ideas of Risch, Norman, Davenport, Trager and others is a heuristic one and develops the integrand f over the differential field K in terms of multivariate rational functions such that
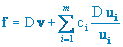
Here v is a quotient of multivariate polynomials, the ui are logarithmic derivatives. Hence, the parallel integration method consists in making educated guesses for the ui and the denominator of v, as well as for the degree of its numerator; thus the calculation of algebraic quantities is reduced to the problem of solving a linear system of equations in order to determine the ci's and constant coefficients of the numerator of v. If the linear equations for the unknown coefficients has a solution, then an integral of f is found. Yet, the nonexistence of a solution does not always imply that f does not have an elementary integral over K but could mean that the guess was wrong. This makes the method although heuristic nevertheless very successful in some CAS such as Maple or Mathematica.
The original version of the program pmint (which stands for Poor Man's Integrator ) is a very short one with less than 100 lines of Maple code for integrating transcendental elementary or special functions.
Because powerful Maple functions (e.g. convert) used do not have a direct correspondence in Mathematica the task rewriting pmint into Mathematica code is not straightforward. However, the Mathematica version of pmint was formulated in 2007 by Luis A. Medina and Alexander Pavlyk at Wolfram Research Inc. Many examples which have been tested with the Maple version of pmint are investigated with the Mathematica implementation of pmint .
It turns out that the Poor Man's Integrator is able to compute even integrals which cannot be handled by the standard integrator implemented in Mathematica or Maple. This is due to the fact that pmint is applicable to special functions (such as Airy, Bessel, Whittaker, Lambert W and Wright Omega functions etc. ). The discussion of the current paper shows the strengths but also some drawbacks of this heuristic approach which can be considered as an extension of the well-established Risch algorithm |
| |
|
|
| |
 |
On the computation of the matrix power
|
| |
|
G.I.Malaschonok, M.V. Starov
(Tambov State University) |
| |
|
|
| |
|
Well known algorithm for the matrix power computation is based on the computation of the roots of characteristic polynomials of this matrix. Victor Robuk proposed an algorithm for the matrix power computation which demands only coefficients of characteristic polynomials and not uses its roots. We show that Robuk's algorithm has exponential complexity and we suggest new algorithm that has polynomial complexity.
|
| |
|
|
| |
 |
Formal Integral and Caustics in the Dynamical
Systems with Two Degrees of Freedom |
| |
|
A.A. Mylläri (Tuorla Observatory, University of Turku, Finland), A.A. Gusev, V.A. Rostovtsev, S.I. Vinitsky
(JINR, Dubna) |
| |
|
|
| |
|
We study the structure of the caustics in dynamical systems with two degrees of freedom. Hénon-Heiles model is used as an example. Caustics could be constructed by numerical integration using the method suggested by T.A. Agekian (1974) that uses the equation for the direction field. Using this method it is possible to get the enveloping curve of the trajectory and caustics of the velocity field. Results of numerical integration are compared with the ones obtained analytically by using formal integral of motion. We use the program LINA (version for Mathematica 6) developed at JINR to construct formal integral of motion. This integral is used (together with the Hamiltonian of the system) to study analytically the evolution of caustics (changes in the structure of the velocity field). As well as for the construction of surfaces of section, results obtained by using formal integral (for small energy) are in agreement with numerical integration.
|
| |
|
|
| |
 |
An upper bound for Differential Nullstellensatz |
| |
|
A.I.Ovchinnikov (MSU and University of Illinois at Chicago), O.D Golubistky (University of Western Ontario), M.V. Kondratieva (MSU), Agnes Szanto (North Carolina State University) |
| |
|
|
| |
|
We discuss the first known bound for orders of differentiations in
differential
Nullstellensatz for both partial and ordinary algebraic differential
equations.
This problem was previously addressed by Seidenberg but no complete
solution was given. Our result is a complement to the corresponding result
in algebraic geometry, which gives a bound on degrees of polynomial
coefficients
in effective Nullstellensatz |
| |
|
|
| |
 |
Towards an algorithmic construction of the ring of
polynomial invariants for the quantum entanglement issue |
| |
|
V.P. Gerdt, A.Khvedelidze and U. Palii (LIT, JINR) |
| |
|
|
| |
|
The problem of the quantum entanglement in composite systems,
i.e. the quantification issue of non-local correlations, which do
not have the classical analogue, reduces to the description of
orbits of the group of local transformations acting on a space of
quantum states. In virtue of the physical requirements this space
is a semi-algebraic set. Therefore the implementation of methods
of the classical theory of invariants, which are well adapted to
the case of linear and algebraic action, demands an additional
analysis as well as a modification of the known computational
algorithms. In the present talk these issues and ways to resolve
the computational difficulties of the construction of the ring of
polynomial invariants are addressed. |
| |
|
|
| |
 |
Approximate summation of rational functions |
| |
|
S. P. Polyakov (Computing Center of Russian Academy of Science |
| |
|
|
| |
|
IAn algorithm for approximate summation of rational functions is proposed. Given a rational function f(x) and a nonnegative number d it constructs a rational function g(x) such that g(x+1)-g(x) may be obtained by deviating the roots of numerator and denominator of f(x) independently by values not exceeding d. |
| |
|
|
| |
 |
Mathematica Package for Simulation of Quantum Circuits |
| |
|
V. P. Gerdt (JINR, Dubna), R.Kragler
(University of Applied Sciences, Weingarten, Germany),
A.N.Prokopenya (Brest State Technical University, Belarus) |
| |
|
|
| |
|
In this paper we present A Mathematica package for simulation of quantum circuits and illustrate some of its facilities by simple examples.
Unlike other Mathematica-based quantum simulators, our package provides a user-friendly graphical interface for representation of quantum circuits,
drawing the corresponding diagrams and computing the circuit unitary matrices. In addition to standard linear algebra-based tools,
our program implements special computer-algebra technique for constructing the multivariable polynomial system of equations that, f
or a circuit composed from the Toffoli and Hadamard gates, uniquely defines the circuit matrix.
Two test quantum circuits are considered to compare our package with other Mathematica-based simulators.
|
| |
|
|
| |
 |
CMUCL based REDUCE |
| |
|
A.M.Raportirenko (JINR, Dubna) |
| |
|
|
| |
|
Common Lisp based computer algebra system REDUCE under
CMUCL interpreter is presented. The concurrent using of
the modules written in Common Lisp and Snandard Lisp
and CMUCL specific questions in compilation and optimization
are discussed.
|
| |
|
|
| |
 |
Indicial Rational Functions for Linear Ordinary Differential
Equations
with Polynomial Coefficients |
| |
|
Abramov S.A. (CC RAS) , Ryabenko A.A.(CC RAS) |
| |
|
|
| |
|
We present an algorithm to construct an indicial rational functions V(z) for a differential equation
an(z)y(n) + · · · + a1(z)y'(z) + a0(z)y(z) = f(z),
where f(z), ai(z) ∈ K[z], K is a field of charachteristic 0. The algoritm is based on a balanced factorization an(z) w.r.t. f(z), a0(z), a1(z),..., a{n-1}(z) with a following sub-partition. An implementation is an improvement of a procedure ratsols from a DEtools package of the computer algebra system Maple. |
| |
|
|
| |
 |
Investigation of solutions of boundary problems for the singular-perturbed differential equation of high order in a field of coulomb potential
|
| |
|
I.V. Amirkhanov, D.Z. Muzafarov, N.R. Sarker, I. Sarhadov, Z.A. Sharipov (JINR, Dubna)
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
Using the system of symbolic computaion MAPLE, the solutions of boundary-value problem for the differential equation of 4-th ordert with small parameter μ at the higher derivative with Coulomb potential are investigated. At μ→0, this equation transfers in а Schrodinger equation. The investigations of eigenvalues and eigenfunctions are held at different values of μ . At any fixed value of μ two types of solutions are obtained : one solution at μ→0 transfers in the solution of Schrodinger equation and the other becomes the boundary layer .
The work has been performed at financial support of the RFBR, grants № 07-01-00738, 08-01-00800 .
|
| |
|
|
| |
 |
Numerical and analytical studying breather type solutions. Problem of the level lines construction
|
| |
|
S.I.Serdyukova ( JINR, Dubna) |
| |
|
|
| |
|
The REDUCE computer algebra system is used to investigate nonstandard linear differential equations arising after averaging the equations describing wave propagation in periodic stratified media. Numerical computations show the existance of breather-type
solutions for equation
Utt = Uxx + ibUttx + Uttxx , 0 ≤ b ≤ 2, being equivalent to a system of two equations with respect real and imaginary parts of U. For numerical solution the differential equations areapproximated by implicite difference equations. At every time step, the stepwise pursuit is prodused. To impliment the matrix stepwise pursuit, symbolic computations are used. For the
limit values of b the asymptotics when t →∞ were proved by using the saddle point method. For intermediate b-values the problem of level lines construction for integrand function
becomes actual. We solve this problem by using the REDUCE system
again.
|
| |
|
|
| |
 |
Investigation of zeros for a class of entire functions
|
| |
|
S.L.Skorokhodov (Computing Centre RAS) |
| |
|
|
| |
|
We consider a parametric family of entire functions F(a; z), defined as an expansion in a complex z-plane:
F(a; z) =∑kzk /( k!) a, 0 <a <1.
These functions arise in the quantum optic problems, statistical mechanics, etc. An important question is a high accuracy of evaluation for the function F(a; z), but the investigation of complex zeros is of special interest. Using the symbolic evaluations enables us to construct approximations for F(a; z) on the base of hypergeometric functions 1_F_1, and as a result, to derive high accurate approximations for the complex zeros. |
| |
|
|
| |
 |
A class of boundary-value problems in polygonal domains: exact and finite
difference solutions
|
| |
|
S.L.Skorokhodov, V.I.Vlasov (Computing Centre RAS) |
| |
|
|
| |
|
We consider the Dirichlet problem for the Poisson equation in plane polygonal domains. The exact solution to the problem is obtained by the use of Trefftz method. The method is based on conformal mapping of the initial domain onto the special polygonal domain, which is disposed on the Riemann surface. Finite-difference solution to the problem is constructed by the use of matrix-sweep method. The main difficulty of the method is connected with the problem of summation the oscillating terms with high amplitude. Using the symbolic evaluations enables us to overcome this dangerous numerical instability. |
| |
|
|
| |
 |
Computation of Bounds for Roots of Orthogonal Polynomials
|
| |
|
D. Stefanescu (University of Bucharest) |
| |
|
|
| |
|
We discuss two methods for computing bounds for the largest roots of orthogonal polynomials. One is based on results on real roots of polynomials, the other on the positivity of the Hessian of hyperbolic polynomials. |
| |
|
|
| |
 |
Combinatorics of monomial orderings and universal Gröbner bases.
|
| |
|
D.A.Pavlov (SpbGTU), N.N. Vassiliev (Steklov Institute of Mathematics at
St.Petersburg) |
| |
|
|
| |
|
The report will state some problems, related to the combinatorics of
finite monomial orderings,
Young tables and diagrams, and the combinatorics of universal Gröbner basis. |
| |
|
|
| |
 |
Permutation binomials over Fp for p<2000
|
| |
|
E.V.Shadrin (SpbGTU), N.N. Vassiliev (Steklov Institute of Mathematics at
St.Petersburg) |
| |
|
|
| |
|
We describe and compute all permutation binomials over finite Fields Fp for p<2000. We present also the tableaux for values of numbers of permutation binomials for p<2000 and describe the statistics for the lengths of cicles for corresponding permutations. |
| |
|
|
| |
 |
Symbolic and numerical methods for definitions a critical parameters
of rotating magnetized polytrophic with a small index
|
| |
|
I.V. Puzynin (JINR), V.P. Tsvetkov, S.A. Mikheev (TvSU) |
| |
|
|
| |
|
In this report represent algorithms and complexes of programs of symbolic and numerical calculations equations witch the critical parameters of rotating magnetized polytrophic with a small index. |
| |
|
|
| |
 |
On efficiency of involutive criteria in computing Boolean Gröbner bases
|
| |
|
V.P.Gerdt , M.V.Zinin ( JINR, Dubna) |
| |
|
|
| |
|
In this paper computational efficiency of applying four involutive criteria in computing Boolean Gröbner bases by the Pommaret division algorithm is studied. In particular, we found that in Boolean rings the criteria are of less importance in comparison to the involutive basis computation in commutative polynomial rings. As this takes place, application of the 2nd and/or 3rd criterion is of more importance then application of the other two criteria. |
| |
|
|
| |
 |
On F5 Algorithm
|
| |
|
A.I.Zobnin
(
Moscow State University, Faculty of Mechanics and Mathematics
) |
| |
|
|
| |
|
The F5 Algorithm for computing Groebner basis was proposed by J.-C. Faugere in 2002 as a new algorithm without reduction to zero. In this algorithm, the input system of polynomials must be homogeneous and regular. The original proof of this algorithm was complicated and intricate, and its "matrix" version was given by M.T. Bardet without proof. We propose a simple proof of this algorithm and discuss the possibility of its extension to the case of arbitrary input polynomials.
|
| |
 |
О субаналитических решениях линейных разностных уравнений с полиномиальными коэффициентами
|
| |
|
С.А.Абрамов ( Вычислительный центр РАН, МГУ) |
| |
|
|
| |
|
Рассматриваются субаналитические секвенциальные решения линейных разностных уравнений с полиномиальными коэффициентами. Результаты получены совместно с М. Баркату, М.Петковшеком и М. ван Хое.
|
| |
|
|
| |
 |
Алгоритм вычисления степенных преобразований для анализа системы ОДУ
в окрестности бесконечно удалённых особых точек
|
| |
|
А.Б.
Арансон
(Научно Исследовательский институт Дальней Радиосвязи, Москва
) |
| |
|
|
| |
|
Рассматривается автономная система ОДУ с полиномиальными правыми частями. Для анализа такой системы в окрестности её неподвижных точек используется метод нормальной формы. Для анализа этим методом окрестностей особых точек, расположенных на бесконечности, надо перевести эти особые точки в конечную область. Это можно сделать с помощью степенных преобразований. В работе предлагается алгоритм вычисления степенных преобразований, использующий многогранники Ньютона-Брюно. Алгоритм реализован в виде набора процедур в системе компьютерной алгебры "Maxima". Рассматривается применение этого алгоритма для анализа системы Хенона-Хейлеса. |
| |
|
|
| |
 |
Комбинаторика мономиальных упорядочений и универсальные базисы Гребнера
|
| |
|
Н.Н. Васильев (ПОМИ РАН), Д.А.Павлов, СПбГПУ
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
В докладе будет рассказано о некоторых задачах, связанных с комбинаторикой конечных мономиальных упорядочений, таблиц и диаграмм Юнга и комбинаторикой универсального базиса Гребнера. |
| |
|
|
| |
 |
Компьютерно-алгебраические аспекты категорий Фукаи
|
| |
|
Н.М.Глазунов (Киевский национальный университет авиации, Украина) |
| |
|
|
| |
|
Категория Фукаи является представлением на языке гомологической и гомотопической алгебры лагранжевых многообразий и их морфизмов. Мы исследуем компьютерно-алгебраические аспекты этих категорий.
|
| |
|
|
| |
 |
Символьно-численный алгоритм редукции двумерной краевой задачи
к обыкновенным дифференциальным уравнениям
|
| |
|
С.И. Виницкий, В.П. Гердт, А.А. Гусев, В.А. Ростовцев,
О. Чулуунбаатар (ОИЯИ, Дубна ) |
| |
|
|
| |
|
Представлен символьно-численный алгоритм
построения асимптотических разложений
редукции двумерной краевой задачи
к системе радиальных дифференциальных уравнений второго порядка с
однородными условиями третьего рода в граничных точках конечного
интервала, используя базис угловых сплюснутых сфероидальных
функций. Построены рекуррентные соотношения для вычисления с
заданной точностью асимптотических разложений искомого решения по
угловой и радиальной переменным при малых и больших
значениях радиальной переменной, включая пороговые значения
спектрального параметра в непрерывном спектре. Эффективность
алгоритма подтверждена тестовыми расчетами и визуализации
асимптотических разложений двумерных решений.
|
| |
|
|
| |
 |
Задача экономизации полиномов многих переменных
|
| |
|
Н.Н. Васильев (ПОМИ РАН)
, В.Ф. Еднерал (НИИЯФ МГУ)
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
Нередко в прикладных задачах приходится многократно вычислять значения полиноминальных или рациональных функций многих переменных. Таковы, например, задачи многомерного интегрирования по фазовому пространству при вычислении вкладов в сечения рассеяния частиц от наборов фейнмановских диаграмм. Часто возникает вопрос об аппроксимации соответствующих полиномов, полиномами с существенно меньшими носителями. Такую задачу иногда называют задачей экономизации полиномов. Частным случаем является хорошо известный метод Ланцоша аппроксимации полинома от одной переменной полиномом меньшей степени. Для полиномов от нескольких переменных нетривиальным моментом является выбор носителя аппроксимирующего полинома. Мы предлагаем подход, в котором носитель аппроксимирующего полинома выбирается на границе многогранника Ньютона-Брюно или вблизи этой границы. Алгоритм многомерной аппроксимации с фиксированным носителем в равномерной метрике основан на сведении к задаче линейного программирования. |
| |
|
|
| |
 |
О роли инволютивных критериев при вычислении булевых базисов Грёбнера
|
| |
|
В.П. Гердт , М.В. Зинин (ОИЯИ, Дубна)
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
В данной работе изучается эффективность применения четырех критериев в инволютивном алгоритме, основаннгом на деления Поммаре, при его применении для построении булевых базисов Грёбнера. Одним из результатов проведенного исследования является тот факт, что при вычислениях в булевых кольцах критерии играют заметно меньшую роль, чем при вычислениях в обычном кольце многочленов над полем целых чисел. Другим результатом исследования является более высокая эффективность 2 и/или 3 критерия по сравнению с двумя остальными. |
| |
|
|
| |
 |
Исследование алгоритма F5
|
| |
|
А.И.Зобнин (
МГУ имени М.В. Ломоносова, Механико-математический факультет
)
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
Алгоритм F5 для вычисления базиса Гребнера был предложен Фожером в 2002 году и позиционировался как алгоритм, в котором не возникает редукций к нулю. Однако корректная работа этого алгоритма гарантировалась только для однородных многочленов, образующих регулярную последовательность. К тому же, обоснование алгоритма оставалось крайне запутанным, а его "матричная" версия, представленная в диссертации Барде, была вовсе без доказательства. В докладе будет предложено простое обоснование этого алгоритма и будет рассмотрен вопрос о его обобщении на случай произвольных образующих. |
| |
|
|
| |
 |
Символьно-численный алгоритм построения матриц стабилизирующего
функционала в задаче восстановления поверхности
|
| |
|
Л.А. Севастьянов, Д.С.Кулябов, М.Г. Кокотчикова (РУДН, Москва) |
| |
|
|
| |
|
При восстановлении поверхности возникает неустойчивость процедуры, которую необходимо исправить. Основываясь на методе регуляризации Тихонова, построим стабилизирующий функционал. Восстановленная поверхность строится по коэффициентам Фурье в разложении по базису полиномов Цернике. В работе представлен символьно-численный алгоритм построения матриц стабилизирующего функционала, реализованный в системе компьютерной алгебры Axiom. |
| |
|
|
| |
 |
Калибровочная инвариантность в дискретных динамических системах
|
| |
|
В.В.Корняк (ОИЯИ, Дубна) |
| |
|
|
| |
|
Фундаментальные законы физики с современной точки зрения описываются калибровочными теориями с непрерывными калибровочными группами. Мы рассматриваем особенности введения калибровочной инвариантности в дискретные динамические системы с конечными множествами состояний. Типичными примерами таких систем являются клеточные автоматы. |
| |
|
|
| |
 |
Mathematica Implementation of M. Bronstein's Poor Man's Integrator
Parallel Integration Method – Risch Norman Algorithm
|
| |
|
R. Kragler (Weingarten Univ. of Applied Sciences, Germany) |
| |
|
|
| |
|
In May 2005 Manuel Bronstein presented on the same CAS seminar in Dubna his implementation of the so-called "Poor Man's Integrator".
The method of "Parallel Integration" which goes back to ideas of Risch, Norman, Davenport, Trager and others is a heuristic one and develops the integrand f over the differential field K in terms of multivariate rational functions such that
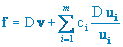
Here v is a quotient of multivariate polynomials, the ui are logarithmic derivatives. Hence, the parallel integration method consists in making educated guesses for the ui and the denominator of v, as well as for the degree of its numerator; thus the calculation of algebraic quantities is reduced to the problem of solving a linear system of equations in order to determine the ci's and constant coefficients of the numerator of v. If the linear equations for the unknown coefficients has a solution, then an integral of f is found. Yet, the nonexistence of a solution does not always imply that f does not have an elementary integral over K but could mean that the guess was wrong. This makes the method although heuristic nevertheless very successful in some CAS such as Maple or Mathematica.
The original version of the program pmint (which stands for Poor Man's Integrator ) is a very short one with less than 100 lines of Maple code for integrating transcendental elementary or special functions.
Because powerful Maple functions (e.g. convert) used do not have a direct correspondence in Mathematica the task rewriting pmint into Mathematica code is not straightforward. However, the Mathematica version of pmint was formulated in 2007 by Luis A. Medina and Alexander Pavlyk at Wolfram Research Inc. Many examples which have been tested with the Maple version of pmint are investigated with the Mathematica implementation of pmint .
It turns out that the Poor Man's Integrator is able to compute even integrals which cannot be handled by the standard integrator implemented in Mathematica or Maple. This is due to the fact that pmint is applicable to special functions (such as Airy, Bessel, Whittaker, Lambert W and Wright Omega functions etc. ). The discussion of the current paper shows the strengths but also some drawbacks of this heuristic approach which can be considered as an extension of the well-established Risch algorithm |
| |
|
|
| |
 |
К вычислению матричной степени
|
| |
|
Г.И.Малашонок, M.В.Старов
(Тамбовский государственный университет им. Г.Р.Державина) |
| |
|
|
| |
|
Алгоритм, который позволяет эффективно вычислять произвольные натуральные степени матрицы, требует вычисления корней характеристического полинома матрицы. В.Робук предложил алгоритм вычисления матричной степени, в котором используются только коэффициенты характеристического полинома матрицы и не требуется находить его корни. В настоящей работе показано, что алгоритм В.Робука имеет экспоненциальную сложность и предлагается другой алгоритм вычисления матричной степени, имеющий полиномиальную сложность. |
| |
|
|
| |
 |
Cимвольно-численные методы в определении критических
параметров вращающихся намагниченных политроп с малым индексом
|
| |
|
Пузынин И.В.(ОИЯИ), Цветков В.П., Михеев С.А.(Тверской государственный университет) |
| |
|
|
| |
|
В докладе излагаются алгоритмы и комплексы программ символьно-численных вычислений уравнений, определяющих критические параметры вращающихся намагниченных политроп. |
| |
|
|
| |
 |
Формальный интеграл и каустики гамильтоновых систем с двумя степенями
свободы
|
| |
|
А. А. Мюлляри (Университет г.Турку, Финляндия), А.А. Гусев, В. А. Ростовцев, С.И. Виницкий (ОИЯИ, Дубна) |
| |
|
|
| |
|
Изучается структура каустик гамильтоновых систем с двумя степенями свободы на примере модели Энона-Хейлеса. Каустики могут быть построены численно, например, используя метод Т.А. Агекяна (1974), который использует уравнения для поля направлений. Применяя этот метод, можно получить огибающую траектории и каустики поля скоростей. В данной работе результаты численных экспериментов сравниваются с результатами, полученными аналитически (без интегрирования траектории) - используя формальный интеграл. Для построения формального интеграла используется программа LINA (версия для Mathematica 6), разработанная в ОИЯИ. Формальный интеграл (вместе с гамильтонианом системы) позволяет аналитически изучать структуру каустик и огибающих. Как и в случае отображения Пуанкаре, результаты, полученные с помощью формального интеграла, согласуются с результатами численного интегрирования. |
| |
|
|
| |
 |
Верхняя граница в дифференциальной теореме Гильберта о нулях
|
| |
|
A.I.Ovchinnikov (MSU and University of Illinois at Chicago), O.D Golubistky (University of Western Ontario), M.V. Kondratieva (MSU), Agnes Szanto (North Carolina State University) |
| |
|
|
| |
|
Мы рассматриваем первую оценку на порядки дифференцирований в дифференциальной теореме Гильберта о нулях как для обыкновенного случая, так и для уравнений с частными производными. Этой задачей занимался Зайденберг, но не предоставил полного решения. Наш результат - дополнение к соответствующему результату из алгебраической геометрии, дающему оценку на степени полиномиальных коэффициентов в эффективной теореме Гильберта о нулях. |
| |
|
|
| |
 |
Алгоритмическое построение кольца полиномиальных инвариантов в задаче квантового перепутывания
|
| |
|
Гердт В.П., Палий Ю.Г., Хведелидзе А.М. (ОИЯИ) |
| |
|
|
| |
|
Задача "квантового перепутывания" составных квантовых систем, т.е. проблема описания нелокальных корреляций, не имеющих классического аналога, сводится к классификации орбит действия группы локальных преобразований на пространстве состояний системы. В силу физических требования это пространство представляет собой полу-алгебраическое многообразие. Поэтому применение методов классической теория инвариантов, хорошо разработанных для действий на линейных пространствах и алгебраических многообразиях, требует дополнительного анализа и модификации известных алгоритмов компьютерной алгебры. В настоящем докладе дается обсуждение данного круга вопросов а также возможных путей разрешения вычислительных трудностей возникающих при построения соответствующего кольца полиномиальных инвариантов.
|
| |
|
|
| |
 |
Приближенное суммирование рациональных функций
|
| |
|
С.П.Поляков (ВЦ РАН) |
| |
|
|
| |
|
Предлагается алгоритм, строящий для рациональной функции f(x) и неотрицательного d такую рациональную функцию g(x), что g(x+1)-g(x) можно получить из f(x) путем независимого сдвига корней числителя и знаменателя на величины, не превосходящие d. |
| |
|
|
| |
 |
Пакет на языке Mathematica для моделирования квантовых схем
|
| |
|
А.Н.Прокопеня (Брестский государственный технический университет, Белоруссия),
В.П Гердт (ОИЯИ, Дубна), Р.Краглер (Университет г. Вайнгартен, Германия) |
| |
|
|
| |
|
В данной работе мы представляем пакет, разработанный на основе системы Mathematica и предназначенный для моделирования квантовых цепей. Его возможности демонстрируются на нескольких простых примерах. В отличие от других подобных симуляторов, наш пакет имеет весьма удобный для пользователей графический способ представления квантовых цепей, их визуализации и вычисления соответствующих унитарных матриц. Кроме стандартных средств линейной алгебры, встроенных в систему Mathematica, в наш пакет включен специальный метод вычисления унитарных матриц цепей, состоящих из логических вентилей Тоффоли и Адамара, основанный на построении полиномиальных систем уравнений со многими переменными, полностью определяющих соответствующие унитарные матрицы. В работе производится сравнение пакета с другими симуляторами на основе двух тестовых квантовых схем.
|
| |
|
|
| |
 |
|
| |
|
А.М.Рапортиренко (ОИЯИ, Дубна) |
| |
|
|
| |
|
В докладе представлена реализация системы компьютерной
алгебры REDUCE в среде Common Lisp с использованием
интерпретатора CMUCL. Рассмотрены вопросы совместного
использования программ, написанных на языках Common Lisp
и Snandard Lisp, а также специфичные для CMUCL особенности
компиляции и оптимизации системы.
|
| |
|
|
| |
 |
Определяющие рациональные функции линейных обыкновенных уравнений с
полиномиальными коэффициентами
|
| |
|
С.А. Абрамов (ВЦ РАН),
А. А. Рябенко (ВЦ РАН) |
| |
|
|
| |
|
Представляется алгоритм построения определяющей рациональной функции $V(z)$ для дифференциального уравнения $$ a_n(z)y^{(n)}+\cdots +a_1(z)y'(z)+a_0(z)y(z)=f(z), $$ где $f(z), a_i(z) \in {\bf K}[z]$, ${\bf K}$ --- поле характеристики 0, на основе уравновешенной факторизации полинома $a_n(z)$ по отношению к $f(z)$, $a_0(z)$, $a_1(z),\dots$, $a_{n-1}(z)$ с последующим подразбиением. Реализация алгоритма в системе Maple является улучшением существующей программы ratsols из пакета DEtools. |
| |
|
|
| |
 |
Исследование решений краевых задач для сингулярно-возмущенного дифференциального уравнения высокого порядка в поле кулоновского потенциала
|
| |
|
И.В. Амирханов, Д.З. Музафаров, Н.Р. Саркар, И. Сархадов, З.А. Шарипов (ОИЯИ, Дубна)
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
Используя систему символьных вычислений MAPLE, исследованы решения краевой задачи для дифференциального уравнения 4-го порядка с малым параметром μ при старшей производной с кулоновским потенциалом. При μ→0 это уравнение переходит в уравнение Шредингера. Проведены исследования собственных значений и собственных функций при различных значениях μ . При любом фиксированном значении μ найдены два типа решений: одно решение при μ→0 переходит в решение уравнения Шредингера, а другое становится погранслойным.
Работа выполнена при финансовой поддержке РФФИ, гранты №№ 07-01-00738, 08-01-00800. |
| |
|
|
| |
 |
Численно-аналитическое исследование решений типа бризер.
Проблема построения линий уровня |
| |
|
C.И.Сердюкова( ОИЯИ, Дубна) |
| |
|
|
| |
|
С применением системы REDUCE исследуются нестандартные линейные дифференциальные уравнения, возникающие при осреднении уравнений, описывающих движение волн периодических в слоистых средах. Численно установлено существование решений типа бризер для уравнения
Utt = Uxx + ibUttx Uttxx, 0 ≤b ≤2,
эквивалентного системе двух уравнений относительно мнимой и вещественной частей U. Дифференциальные уравнения аппроксимируются неявными разностными уравнениями. На каждом шаге по времени проводится прогонка. Символьные вычисления используются для реализации матричной прoгонки. Для предельных значений
b с помощью метода перевала получена асиптотика решений при t→∞. Для промежуточных значений параметра становится актуальной проблема построения линий уровня подинтегральной функции, которая также решается применением системы REDUCE.
|
| |
|
|
| |
 |
Исследование нулей одного класса целых функций |
| |
|
С.Л.Скороходов (Вычислительный центр РАН) |
| |
|
|
| |
|
Рассматривается однопараметрическое семейство целых функций F(a; z),
задаваемых
своим разложением в комплексной плоскости z:
F(a; z) =∑kzk /( k!) a, 0 <a <1.
Такие функции и родственные им возникают в ряде задач квантовой оптики,
статистической механики и др. Весьма важным вопросом здесь является
достижение высокой точности вычислений F(a; z), однако особый интерес
вызывает исследование комплексных нулей этих функций.
С использованием символьных преобразований в работе построены аппроксимации
функций F(a; z) в виде комбинаций обобщенных гипергеометрических функций 1_F_1,
что позволило получить высокоточные приближения к исследуемым нулям.
|
| |
|
|
| |
 |
Один класс краевых задач в полигональных областях: сравнение точного и
разностного решений |
| |
|
В.И.Власов, С.Л.Скороходов (Вычислительный центр РАН) |
| |
|
|
| |
|
Рассматривается задача Дирихле для уравнения Пуассона в плоских многоугольных областях. Точное решение задачи получено с помощью метода Треффца, основанного на построении конформного отображения исходной области на специальную многоугольную область, расположенную на римановой поверхности. Разностное решение задачи строится с помощью метода матричной прогонки. Возникающее здесь явление суммирования больших знакопеременных слагаемых приводит с сильной численной неустойчивости. Использование символьных преобразований позволяет эффективно преодолевать эту трудность.
|
| |
 |
Computation of Bounds for Roots of Orthogonal Polynomials
|
| |
|
D. Stefanescu (University of Bucharest, Romania) |
| |
|
|
| |
|
We discuss two methods for computing bounds for the largest roots of orthogonal polynomials. One is based on results on real roots of polynomials, the other on the positivity of the Hessian of hyperbolic polynomials. |
| |
|
|
| |
 |
Новый блочный алгоритм для решения разреженных систем линейных уравнений над GF(2) |
| |
|
М.А. Черепнев( мехмат МГУ) |
| |
|
|
| |
|
Предлагаемый алгоритм построен с использованием блочных аппроксимаций Паде.
Время работы алгоритма при параллельной организации вычислений оценивается величиной
max{N^2d/n, O(N^2)},
где N - размер матрицы системы, n - размер блока, d - оценка на число единиц
в строках матрицы.
|